WHAT IS CANCER?
Normal body cells follow a normal cell cycle and will die off eventually. Cancer cells are“immortal”—they avoid programmed cell death. Cancer cells also have unregulated growth, and will invade other tissues. Theoretically, any cell in the body can become cancerous.
WHAT CAUSES CANCER?
There are many different causes, ranging from genetic, to environmental, to harmful effects from different substances. It is very important to be vigilant about these risks to our health.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), tobacco smoke is linked to 80% – 90% of all lung cancers. In the United States, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in both men and women.
In Asia, liver cancer is one of the most common cancers. According to epidemiological studies, chronic infection with hepatitis B causes about 50% – 60% of all cases of liver cancer worldwide.
50% of all gastric cancers happen in Asia. Research says it may be connected to diet, such as traditional pickled or salted foods.
HOW FAST DO CANCER CELLS GROW?
Like any other cell, a cancer cell will divide from one into two, from two into four, and so forth. However, cancer cells do not divide at the same rate as other cells, nor do they divide as fast as bacteria. Some types of cancer cells, depending on how strong your immune system is, may multiply every few months. Research shows that for various types of lung cancer, the cancer cells multiply on average every four to 10 months, while some cancer cells take even longer to multiply.
I AM STILL YOUNG; DO I HAVE TO WORRY ABOUT CANCER?
With our limited technology today, about two-thirds of the development of a cancer remain undetectable by the patient or the doctor. A tumor needs to be about 1 cm, consisting of about one billion cancer cells, before we can see it on an x-ray. If we use a better imaging technique, such as a CT scan, it only needs to be about 1 mm, but by that time, there are already about one million cancer cells there.
In fact, the term “early-stage cancer” is misleading because the patient may think the cancer only happened recently. It is more likely that the cancer has been present for several years already. For example, for a lung cancer to be detectable with modern technology, the tumor would probably have been growing slowly for the past 10 – 20 years. Therefore, if we detect lung cancer at the age of 40, the cancer cells may have already been present in the body since the early twenties.
Our immune system works hard to kill cancer cells as they arise, but it is not perfect. To stay healthy, we need to cultivate a healthy lifestyle since young.

IS THERE NO HOPE FOR CANCER?
With the advancement in different treatments, the five-year survival rates for cancer are getting better.
For your reference, this is a chart detailing the five-year survival rates for various types of cancer.
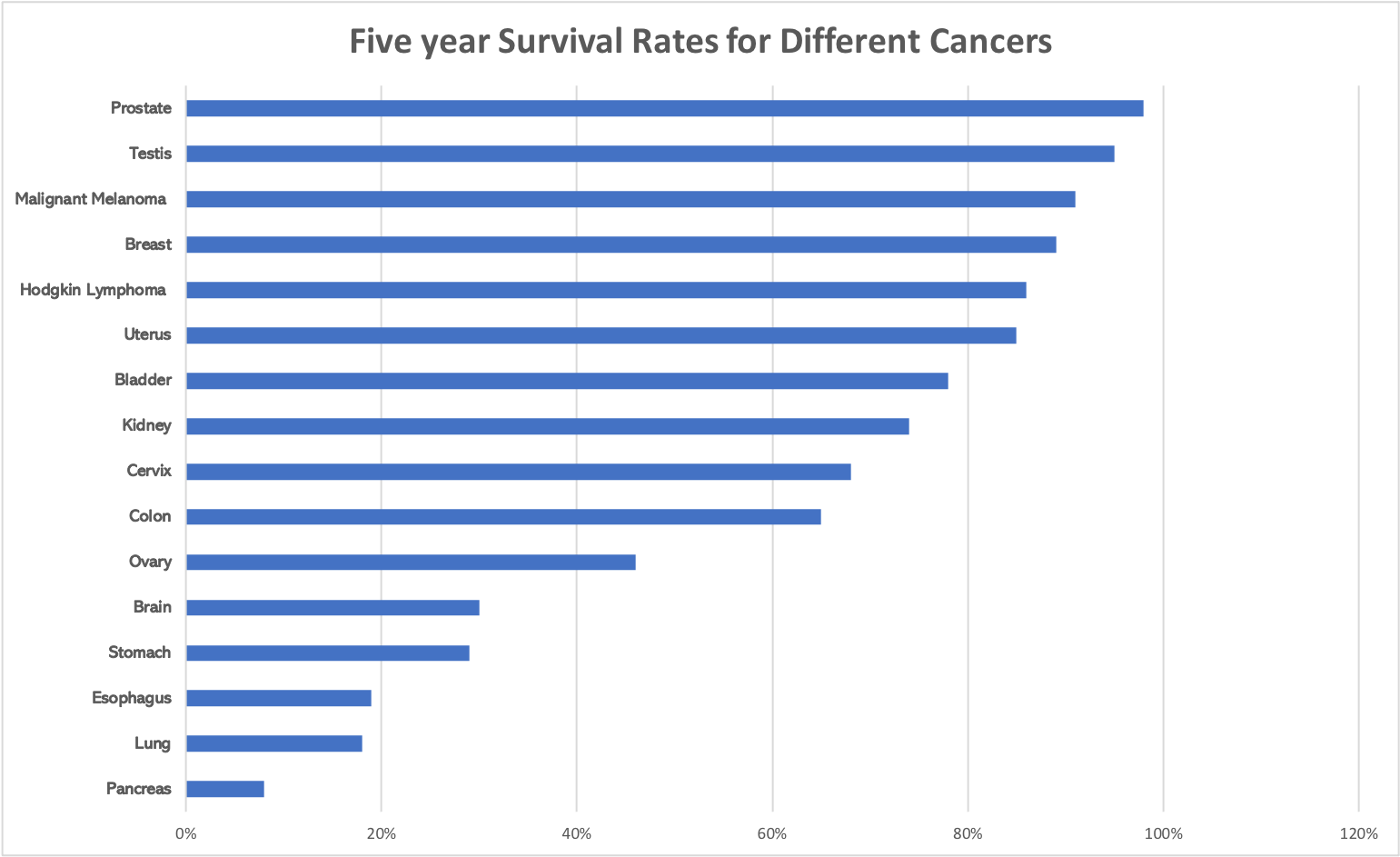
Source : SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2013, National Cancer Institute
Over time, the five-year survival rates may improve with new targeted cancer therapies.
WHAT ARE TARGETED CANCER THERAPIES?
Traditionally, when people think of cancer treatments, they think of chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses drugs that target different phases of the cancer cell cycle. The measure of worth for chemotherapy lies in the length of time it can prolong a cancer patient’s life.
Targeted cancer therapies are medications that work to stop cancer by targeting specific molecules that are necessary for the spread and the growth of certain cancers.
There are many different types of targeted cancer therapies, but one of the most promising is targeted immunotherapies. This new class of cancer treatments triggers the immune system to destroy cancer cells through various methods. For example, CAR T-Cell Immunotherapy modifies one of our immune cells, the T cell, to target and kill cancer cells. Bispecific antibodies, another type of immunotherapy, use different antibodies to destroy tumors.
At the bright new frontier of cancer treatment, immunotherapies use our body’s own doctor—our immune system. Even though researchers and doctors are making new progress in cancer treatment, prevention is always better than cure.

WHAT ARE PHYTOCHEMICALS?
Phytochemicals are nutrients found only in plants. Plants produce phytochemicals to protect themselves from ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
For humans, phytochemicals can be used to help fight against cancer. At almost every step along the pathway to cancer, there are one or more phytochemicals that can slow or reverse the process. So, consuming a wide variety of phytochemicals is better for the immune system.
WHAT ARE SOME EXAMPLES OF THE ACTIONS OF PHYTOCHEMICALS?
Broccoli, cabbage and cauliflower contain sulforaphane, which can help keep cancer-causing agents away from cells. Sulforaphane also boosts your body’s ability to remove cancer-causing agents. Soy contains genistein, which helps prevent cancer cells from receiving the nutrients they need to grow. Limonin and nomilin, phytochemicals in citrus fruits, can help prevent the spread of cancer throughout the body.
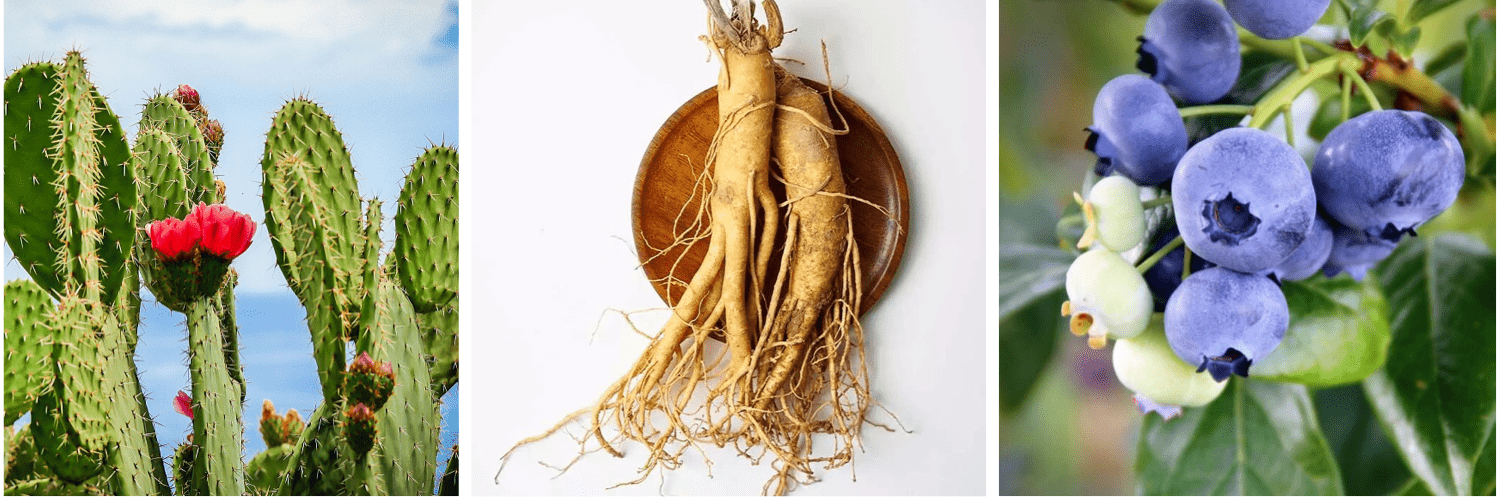
Cactus contains various phytochemicals such as phenolic acid and flavonoids. Research shows that cactus has anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects, while also helping to lower blood glucose and cholesterol levels.
Ginseng also contains a wide variety of phytochemicals, including ginsenosides and saponins. Ginseng contributes to antioxidant activity, as well as having potentially anti-diabetic effects.
Research has shown that phytochemicals can help enhance the immune system, reduce inflammation, prevent processes that lead to cancer, prevent DNA damage, and reduce oxidative damage to cells, as well as many other benefits. These are merely the effects that research has identified; there are more benefits yet to be discovered.

WHY DO I NEED A WIDE VARIETY OF PHYTOCHEMICALS?
Every phytochemical may help inhibit certain phases of cancer. There are many pathways to cancer; a single phytochemical can only prevent one pathway. To comprehensively improve the body’s resistance to cancer, we need to consume a large amount as well as a wide variety of phytochemicals.
There are thousands of phytochemicals, and scientists have only just discovered the tip of the iceberg. So far, research strongly suggests that eating foods high in phytochemicals has a positive benefit on health, and can help prevent diseases such as heart disease, cancer, type 2 diabetes as well as certain neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
WHICH FOODS CONTAIN PHYTOCHEMICALS?
Phytochemicals are present in all plant foods. Fresh greens, cactus, ginseng, and fruits like blueberries are some examples of plant foods that contain a wide range of phytochemicals.
The American Institute for Cancer Research and the World Cancer Research Fund has shown that a healthy lifestyle and diet alone can prevent up to 30% – 40% of cancers. Research shows that a diet containing at least 400 grams of vegetables and fruits per day can reduce the risk of various types of cancers, including cancers of the oral cavity, esophageal cancers, stomach and colon cancers. It can also reduce the risk of other health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
In conclusion, we need a healthy lifestyle, complete with a healthy diet rich in vegetables and fruits, and regular exercise to stay healthy.
References can be found at www.eleadglobal.com.