

WHAT ARE IMMUNOMODULATING POLYSACCHARIDES?
Polysaccharides are present in both the plant and animal kingdoms. They are, at the simplest level, complex carbohydrates made up of monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds. Several major polysaccharides can modulate the immune system. These polysaccharides are often associated with mushrooms. Multiple studies have been done over years, showing that mushrooms are exceptionally rich in polysaccharides.
WHAT ARE THE MANY FUNCTIONS OF IMMUNOMODULATING POLYSACCHARIDES?
Polysaccharides work to help directly influence our immune system so that we can defend ourselves against cancer, and viral or bacterial infections. It helps enhance our immune cells by helping them work or by helping them regenerate a little bit faster.
HAS ANY RESEARCH BEEN DONE ON POLYSACCHARIDES?
There are hundreds of thousands of research papers on polysaccharides published throughout the world. Even as early as the 1980s, the Japanese Pharmaceutical Council has recognized and approved lentinan, a polysaccharide found in shiitake mushrooms, as an adjunct for chemotherapy. It is used as a biological response modifier for the treatment of stomach cancer.
Many other polysaccharides are undergoing further research and studies to evaluate their use in treating diseases, such as cancer.

WHAT RESEARCH IS THERE ON SHIITAKE MUSHROOM?
Key Points:
Main polysaccharides: Lentinan and Lentinus edodes mycelium (LEM)
Lentinan can help you fight against bacterial and viral infections, as well as cancer.
LEM can help the immune system recover from damage, for example, after radiotherapy and stress due to chronic illness. It can also help protect different parts of your body, such as your liver, through antioxidant-like actions.
Full Text:
Today, shiitake mushroom is one of the most widely researched mushrooms in the world. Studies have focused on two main extracts from shiitake mushroom—lentinan and LEM.
Stomach cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death worldwide, and is the second most common cancer in Eastern Asia. The rates of stomach cancer in Asia are the highest in the world. Multiple studies have shown that using lentinan in combination with chemotherapy improves the overall survival rates of patients with stomach cancer. In fact, some studies have shown that using chemoimmunotherapy with lentinan increased median overall survival by as much as 95%, even in those with liver metastasis.
That’s not all lentinan can be used for. Lentinan has many immunopotentiating properties, such as boosting the function of natural killer (NK) cells and increasing the production of gamma interferon—this helps us fight against cancer, and bacterial and viral infections. In Japan, lentinan has been used for adjunctive treatment, from HIV to various types of cancer, such as skin, breast, colorectal, cervical and others. Lentinan has also demonstrated some antibacterial properties.
LEM has the potential to help the immune system recover from radiation-damaged bone marrow due to cancer treatment. Research suggests that LEM can help the immune system recover after it has been weakened by chronic illnesses, such as chronic fatigue syndrome, or medical treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Research published in the IN VIVO: International Journal of Experimental and Clinical Pathophysiology and Drug Research shows that LEM, likely through antioxidant-like actions, has a protective effect against liver injury.

WHAT RESEARCH IS THERE ON MAITAKE MUSHROOM?
Key Points:
Main polysaccharide: D-fraction
Maitake mushroom can promote the activity of the different cells of the immune system as well as their chemical secretions. By doing this, it helps boost the immune system against viral and bacterial infections; assists in cancer treatment, and helps prevent cancer relapse.
D-fraction, a part of the polysaccharides in maitake mushroom, can stop normal cells from becoming cancerous. Maitake mushroom also has promising potential in lowering blood pressure and preventing diabetes.
Full Text:
Maitake mushroom promotes the activity of immune cells, such as macrophages—the leukocytes that identify and engulf foreign invaders in the body; natural killer (NK) cells, which identify and kill tumor cells; and cytotoxic T cells. Maitake mushroom also activates cytokines, such as interleukin-1, interleukin-2, and lymphokines, which support the body’s fight against infections, AIDS, and cancer. Therefore, the maitake mushroom not only boosts the immune system against viral and bacterial infections, it also assists in cancer treatment, and in helping to prevent cancer relapse.
In one notable study, scientists conducted experiments to see if D-fraction, the part of polysaccharides in maitake mushrooms that contain potent antitumor activities, could stop normal cells from becoming cancerous. In their experiment, a carcinogen was given to experimental animals to induce cancer. These animals were split into three groups—Group A was given normal food, Group B was given food enriched with maitake powder, and Group C was given food enriched with D-fraction polysaccharide. After 60 days, the scientists examined the liver for tumors. The results were as follows: the number of tumor cells in Group A was 100%, in maitake Group B, 22.2% had liver tumors, in D-fraction Group C, only 9.7% had liver tumors. This suggests that the D-fraction polysaccharide from maitake mushrooms was effective in reducing the risk of cancer.
There’s more! Maitake mushrooms have promising antihypertensive and antidiabetic effects as well!

WHAT RESEARCH IS THERE ON AGARICUS BLAZEI MURRILL (ABM) MUSHROOM?
Key Points:
Main polysaccharides: beta-1,3 D-glucan and beta-1,6 D-glucan
The polysaccharides in ABM mushroom help boost the immune system by increasing the number of immune cells in the body. As immune cells help fight and kill cancer cells, a greater number of immune cells can lead to a lower number of cancer cells generated in the body. In addition to helping us fight cancer, ABM mushrooms also have powerful antiviral and antibacterial effects, and thus also help us fight off viral and bacterial infections.
Full Text:
ABM mushrooms are rich in beta-1,3 D-glucan and beta-1,6 D-glucan, two polysaccharide compounds. These polysaccharides help boost the immune system by increasing the number of immune cells in the body. As immune cells help fight and kill cancer cells, a greater number of immune cells can lead to fewer cancer cells being generated in the body. Research at the King Drew Medical Center of UCLA found that ABM mushroom increases the total amount of immune cells in the body, and also boosts the function of individual natural killer (NK) cells. Research done in Japan, Hong Kong, and the United States suggests that polysaccharides in ABM mushrooms stimulate lymphocyte T-cell and helper T-cell production in the experimental animals.
Research done at the Medical Department of Tokyo University, the National Cancer Center Laboratory, and the Tokyo College of Pharmacy suggests that ABM has powerful antitumor properties. Research was done with mice known to have cancerous tumors. When these mice were fed ABM mushroom powder, the tumors were eliminated in about 90% of the mice.
ABM mushrooms boost the immune system so that it can better help prevent the growth and spread of cancer cells.
In addition to helping us fight cancer, ABM mushrooms have powerful antiviral and antibacterial effects, and thus helps us fight off viral and bacterial infections.
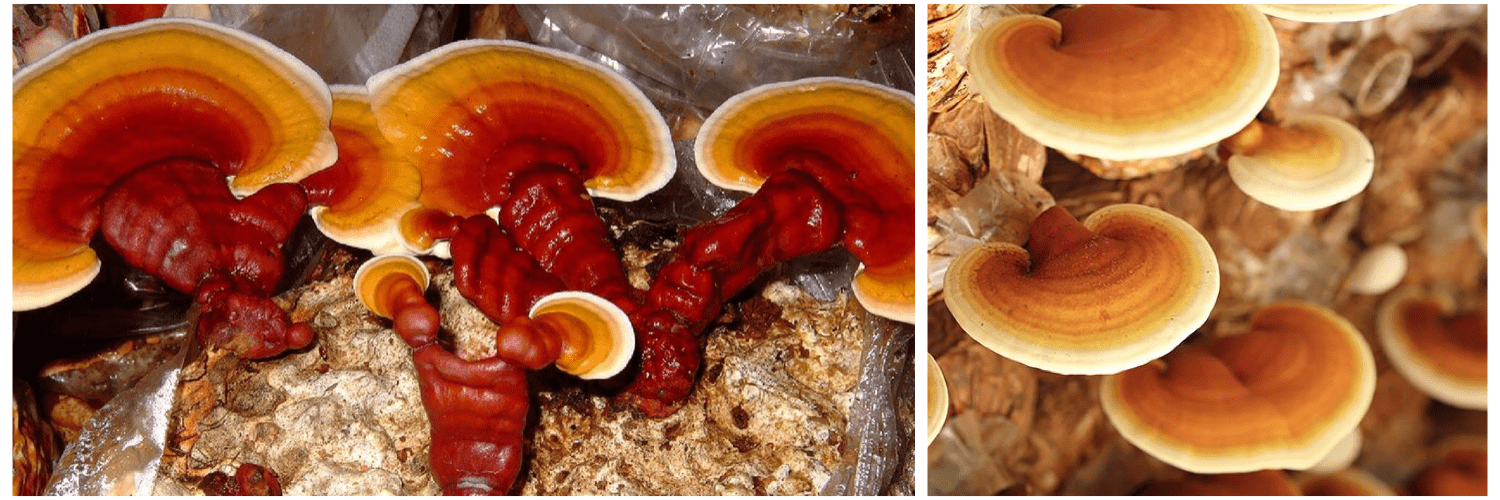
WHAT RESEARCH IS THERE ON REISHI MUSHROOM?
Key Points:
Reishi mushroom, also known as Ganoderma mushroom, has been used to reduce the side effects of cancer chemotherapy, increase survival rates, reduce the spread of metastasis, reduce the risk of cancer recurrence, and improve the overall quality of life of cancer patients. In addition to boosting the immune system and helping to protect you from cancer, reishi mushrooms have also demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects, which may help with diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
Full Text:
Reishi mushroom, also known as Ganoderma mushroom, has great potential in the prevention and treatment of cancer. It has been used to reduce the side effects of cancer chemotherapy, increase survival rates, reduce the spread of metastasis, reduce the risk of cancer recurrence, and improve the overall quality of life of cancer patients. It can be used together with chemotherapy to help reduce the latter’s unpleasant side effects, such as fatigue, weight loss, poor appetite, hair loss, and bone marrow suppression that could lead to a greater risk of dangerous infections.
In terms of cancer prevention, researchers in Japan tested 58 basidiomycetes mushrooms. Out of all of these mushrooms, the reishi mushroom was the most effective in killing cancer cells in their rodent and human cell models.
Research done in the United States suggests that the reishi mushroom helps stop the growth and spread of cancer through various methods.
In a systematic review done in the United Kingdom, looking at a wide range of studies, it was noted that across multiple randomized controlled trials, simply adding reishi mushroom extract to the anticancer regimen of patients increased the patients’ response to chemotherapy or radiotherapy by about 1.27 times, as compared to those without. It was also found that patients who received reishi mushroom extract experienced stimulation of their immune systems in the form of increased CD3, CD4, and CD8 lymphocyte percentages, as well as increased NK cell activity. These patients’ quality of life was improved and the severity of the side effects from cancer treatments was reduced.
In addition to boosting the immune system and helping to protect you from cancer, reishi mushrooms have demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects. There is emerging evidence that reishi mushroom holds promise in treating neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease or Alzheimer’s disease, thanks to its anti-inflammatory effects.

WHAT RESEARCH IS THERE ON CORIOLUS VERSICOLOR MUSHROOMS?
Key Points:
Main polysaccharides: Polysaccharide-K (PSK), also known as Krestin?, and polysaccharide peptide (PSP)
PSK has been shown to have antimicrobial, antiviral, and antitumor properties. PSP has a more potent anticarcinogenic effect and immunological regulator effect than PSK. The polysaccharides in Coriolus versicolor mushroom can help suppress tumor growth and spread, and when given with chemotherapy, may enhance the actions of the chemotherapy medications.
Full Text:
Coriolus versicolor is one of the most widely researched mushrooms in the world. It contains various beneficial polysaccharides. Noteworthy polysaccharides are polysaccharide-K (PSK), also known as Krestin?, and polysaccharide peptide (PSP).
PSK has been shown to have antimicrobial, antiviral, and antitumor properties. PSP has a more potent anticarcinogenic effect and immunological regulator effect than PSK.
Significant research has been done on both laboratory animals and humans.
A significant study published in 1991 demonstrates the antitumor properties of PSK. Experimental animals known to have tumors were given an injection of PSK, which inhibited the growth of tumors. In a different study, PSK was given to animals with colon cancer. The animals showed an improved T-cell response and suppressed tumor growth.
In human studies, PSK was most often given alongside chemotherapy. A randomized study published in The Lancet, one of the world’s most prestigious research journals, showed that when PSK was added to standard chemotherapy, about 59% to 70% of 262 stomach cancer patients experienced five years free from cancer. PSK also helps with other types of cancer. One study showed that when PSK was added to the chemotherapy of patients with stage-I or stage-II non-small cell lung cancer, there was an increase in 5-year survival rate from 16% to 39%. In those with stage-III cancer, 5-year survival rate increased from 5% to 16%. In other studies, PSK has also been shown to inhibit the growth of leukemia cells.
Not only does PSK help suppress tumor growth and spread, it may also enhance the actions of the chemotherapy medications when given along with chemotherapy.

WHAT RESEARCH IS THERE ON CORDYCEPS SINENSIS/CORDYCEPS MYCELIUM?
Key Points:
Main polysaccharides: cordycepin and cordycepic acid
Cordyceps polysaccharides have antioxidant, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory effects. They have the potential to regulate immune functions, thus helping to prevent the spread of cancer. In addition, they can help lower blood lipid levels, and they have strong antioxidant activity to protect cells against the damage of free radicals.
Cordyceps sinensis can help calm an overstimulated immune system. In this sense, it may help with a weak immune system and autoimmune disorders.
Clinical studies have shown that Cordyceps sinensis can help protect against arrhythmia, heart failure, as well as help lower cholesterol levels. Patients who have kidney issues or lung problems, such as asthma, can also benefit from this mushroom.
Full Text:
Cordyceps sinensis has long been considered one of the most valuable mushrooms in the world. It is rich in nutrients, such as adenosine, amino acids, ergosterol, and polysaccharides.
Cordyceps polysaccharides have antioxidant, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory effects. They have the potential to regulate immune functions, thus helping to prevent the spread of cancer. In addition, they can help lower blood lipid levels, and have strong antioxidant activity to protect cells against the damage of free radicals.
Cordycepin and cordycepic acid are active components of Cordyceps sinensis. They have immunoregulatory, anticancer, antiviral, and anti-infection effects. In fact, the U.S. National Cancer Institute has introduced cordycepin as a potential new anticancer drug to undergo further investigations and development. Cordyceps sinensis could strengthen the immune system of patients who have undergone damaging procedures, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, or stressful events, such as surgery.
Not only can Cordyceps sinensis help boost the immune system, it can also help calm an overstimulated immune system. In this sense, it may help with weak immune systems and autoimmune disorders.
The stories of Cordyceps sinensis being taken in ancient times for more energy and stamina have merit! Cordyceps sinensis greatly increases the amount of two very powerful antioxidant enzymes—superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase. It can also increase the ratio of adenosine triphosphate to inorganic phosphate in our liver, improve the use of oxygen by our cells, and boost the function of our adrenal cortex. This means that it can help improve exercise performance, or for those who suffer from chronic fatigue syndrome, help give them a bit more energy.
Clinical studies have shown that Cordyceps sinensis can help protect against arrhythmia and heart failure, as well as lower cholesterol levels. Patients who have lung problems, such as asthma, can also benefit from Cordyceps sinensis.
Researchers have also looked into how Cordyceps sinensis can help those with kidney problems. In a study done in China, chronic kidney failure patients who were treated with Cordyceps sinensis for 30 days had significant improvement in their kidney function.
Cordyceps sinensis has great nutritional benefits that boost our health—it’s not hard to realize why it’s such a precious mushroom!
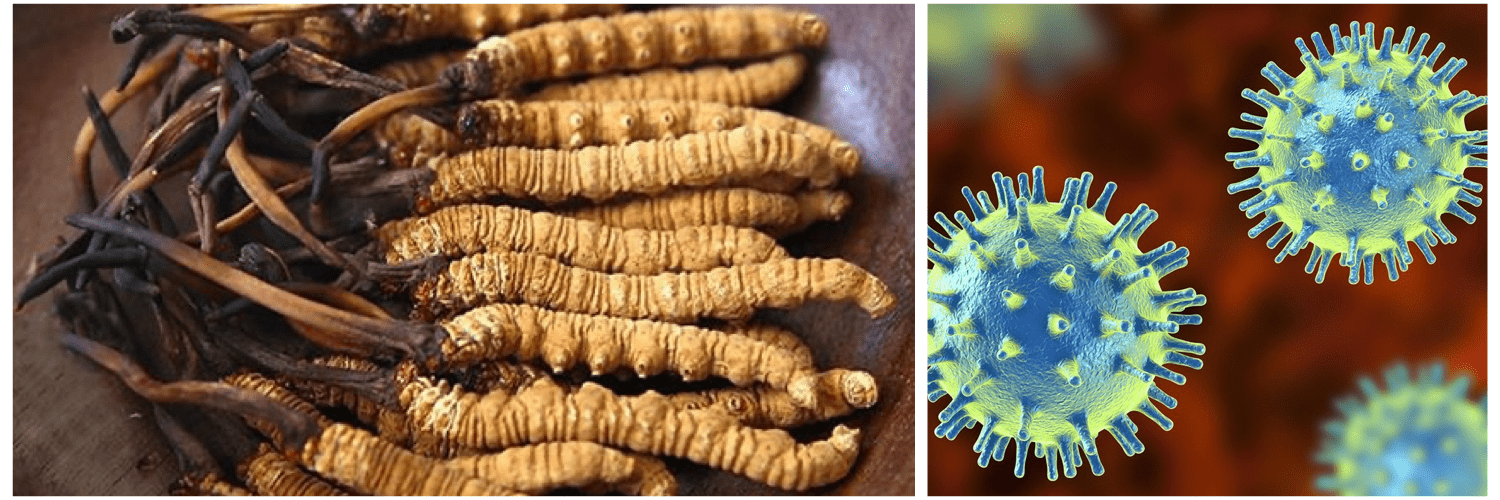

WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN WILD CORDYCEPS SINENSIS AND CULTIVATED CORDYCEPS MYCELIUM?
Cordyceps sinensis is a very rare and valuable mushroom. It has been long regarded, since the Qing Dynasty, to possess amazing capabilities to nourish the body.
Wild cordyceps grow on mountains at an altitude of about 4,000 meters above sea level. As you can imagine, this makes it difficult to collect. In addition, it can’t be cultivated—this makes it very expensive. However, the quality of wild cordyceps cannot be guaranteed. The market is filled with cordyceps contaminated by heavy metals in the soil, or cordyceps contaminated with lead inserted by unscrupulous sellers looking to increase weight and profit.
On the other hand, the mycelium of Cordyceps sinensis can be cultivated. The nutritional value is considerable, but only cordyceps mycelium of certain verified species of cordyceps, cultured under strict conditions, will match the nutritional value of Cordyceps sinensis. Of over 400 species, only about 10 species of cordyceps have the amount of cordycepin, a polysaccharide, deemed to be of nutritional value.
DO I NEED A VARIETY OF POLYSACCHARIDES OR JUST ONE POLYSACCHARIDE IN A HIGH CONCENTRATION?
Each polysaccharide can help prevent a certain stage of cancer development, and different polysaccharides have their own effects on improving our health. By taking a wide variety, you can help enhance different aspects of your immune system.
Your immune system is made up of various different organs, cells, and chemical secretions. It is like your personal army, and like an army, you have your air force, your navy, your soldiers, and your ammunition. You need everything to be in working order and working together. We have to take care of every part of our immune system. To do this, one of the best ways is to take in a wide variety of polysaccharides to help enhance all the different parts of our immune system.
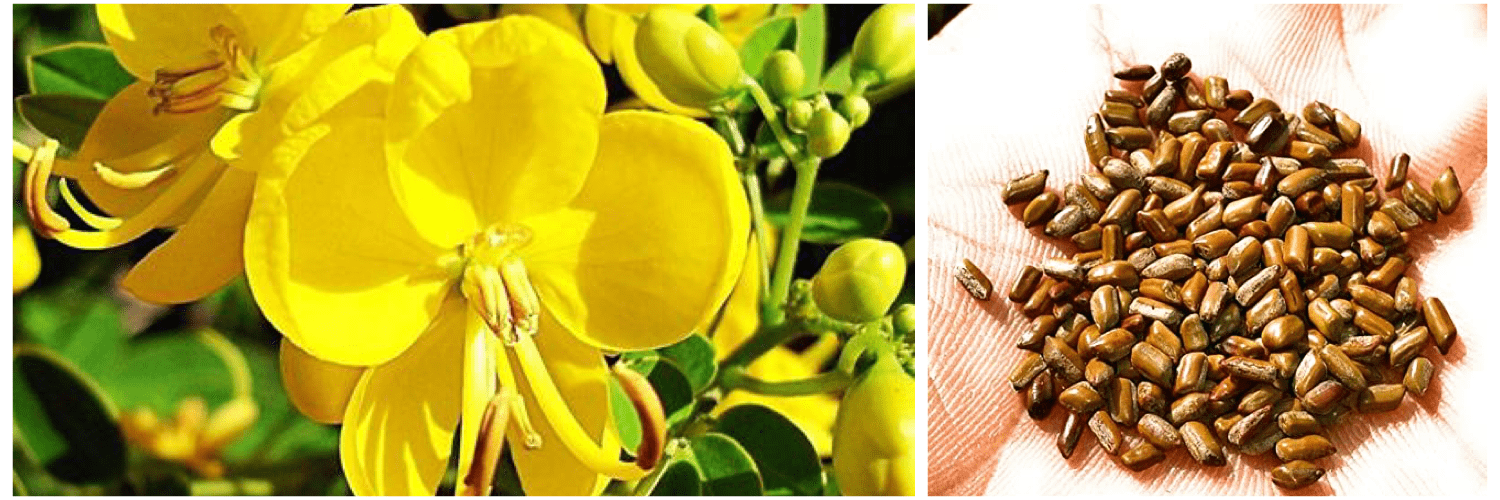

WHAT RESEARCH IS THERE ON CASSIA TORA?
Key Points:
Cassia tora has been demonstrated to have a wide range of antimicrobial activity. It can also help keep the heart healthy, and help prevent atherosclerosis. In addition to the heart, Cassia tora can also help protect against liver damage, and control blood sugar levels.
Full Text:
Cassia tora has been demonstrated to have a wide range of antimicrobial activity. Multiple studies have shown it to be effective against gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria, and fungi. Researchers in the United States and India suggest that it can be used in the formulation of antimicrobial agents for the treatment of bacterial and fungal infections, such as gonorrhea, pneumonia, and even eye infections.
Cassia tora can also help keep the heart healthy and help prevent atherosclerosis. Research done in India with experimental animals noted that Cassia tora had significant lipid-lowering effects. Rats given Cassia torahad lower levels of lipid in their blood plasma and liver. Cassia tora can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and increase HDL cholesterol levels.
Studies done with rats with liver damage showed that those receiving Cassia tora had lower liver damage markers than those which did not. This suggests that Cassia tora has significant liver protection properties.
Cassia tora also has the potential to improve glycemic control. According to a study done in Korea, rats with diabetes which were given Cassia tora seed butanol fraction had better blood glucose control than those which did not.
References can be found at www.eleadglobal.com.